Install a database (Mysql or Oracle). Create a table which should contain at least the following fields: name, password, email-id, phone number Write a java program/servlet/JSP to connect to that database and extract data from the tables and display them. Insert the details of the users who register with the web site, whenever a new user clicks the submit button in the registration page
Install a database (Mysql or Oracle). Create a table which should contain at least the following fields: name, password, email-id, phone number Write a java program/servlet/JSP to connect to that database and extract data from the tables and display them. Insert the details of the users who register with the web site, whenever a new user clicks the submit button in the registration page
AIM: Install a database (Mysql or Oracle).
Create a table which should contain at least the following fields: name, password, email-id, phone number (these should hold the data from the registration form).
Practice 'JDBC' connectivity.
Write a java program/servlet/JSP to connect to that database and extract data from the tables and display them. Experiment with various SQL queries.
Insert the details of the users who register with the web site, whenever a new user clicks the submit button in the registration page (week2).
DESCRIPTION:
JDBC Driver Types
There are four types of JDBC drivers in use:
Type 1: JDBC-ODBC Bridge
A Type 1 JDBC-ODBC Bridge provides application developers with a way to access JDBC drivers via the JDBC API. Type 1 JDBC drivers translate the JDBC calls into ODBC calls and then send the calls to the ODBC driver. Type 1 JDBC drivers are generally used when the database client libraries need to be loaded on every client machine.
Type 2: Native API/Partly Java Driver
A Type 2 Native API/Partly Java Driver is a partial Java driver because it converts JDBC calls into database specific calls. Type 2 Native API/Partly Java Driver communicates directly with the database server.
Type 3: Pure Java Driver
A Type 3 Pure Java Driver works in a three tiered architecture. The JDBC calls are passed via the network to the middle tier server. This server translates the calls to the database specific native interface to further request the server. JDBC drivers available from Simba are Type 3 drivers.
Type 4: Native Protocol Java Driver
The type 4 driver is written completely in Java and is hence platform independent. It is installed inside the Java Virtual Machine of the client. It provides better performance over the type 1 and 2 drivers as it does not have the overhead of conversion of calls into ODBC or database API calls. Unlike the type 3 drivers, it does not need associated software to work.A Type 4 Native Protocol Java Driver converts JDBC calls into the database specific calls so that the client applications can communicate directly with the server.
PROGRAM:
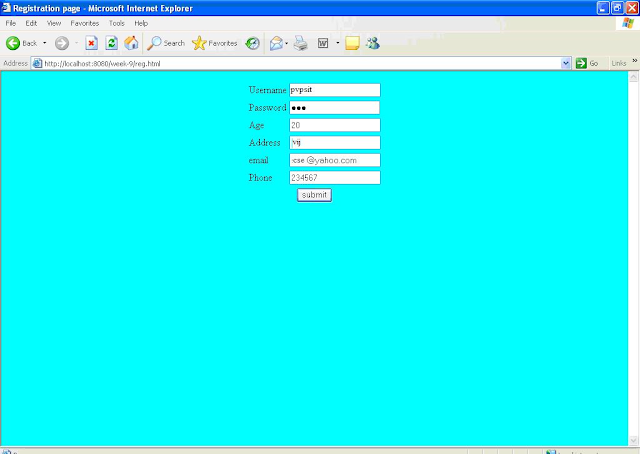
Registration.html:
<html>
<head>
<title>Registration page</title>
</head>
<body bgcolor="#00FFFf">
<form METHOD="POST" ACTION="register">
<CENTER>
<table>
<center>
<tr> <td> Username </td>
<td><input type="text" name="usr"> </td> </tr>
<tr><td> Password </td>
<td><input type="password" name="pwd"> </td> </tr>
<tr><td>Age</td>
<td><input type="text" name="age"> </td> </tr>
<tr> <td>Address</td>
<td> <input type="text" name="add"> </td> </tr>
<tr> <td>email</td>
<td> <input type="text" name="mail"> </td> </tr>
<tr> <td>Phone</td>
<td> <input type="text" name="phone"> </td> </tr>
<tr> <td colspan=2 align=center> <input type="submit" value="submit"> </td> </tr>
</center>
</table>
</form>
</body>
Login.html
<html>
<head>
<title>Registration page</title>
</head>
<body bgcolor=pink> <center> <table>
<form METHOD="POST" ACTION="authent">
<tr> <td> Username </td>
<td><input type="text" name="usr"></td> </tr>
<tr> <td> Password </td>
<td> <input type="password" name="pwd"> </td> </tr>
<tr> <td align=center colspan="2"><input type="submit" value="submit"></td> </tr>
</table> </center>
</form>
</body>
</html>
Ini.java:
import javax.servlet.*;
import java.sql.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Ini extends GenericServlet
{
private String user1,pwd1,email1;
public void service(ServletRequest req,ServletResponse res) throws ServletException,IOException
{
user1=req.getParameter("user");
pwd1=req.getParameter("pwd");
email1=req.getParameter("email");
res.setContentType("text/html");
PrintWriter out=res.getWriter();
try
{
Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver");
Connection con=DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:oracle:thin:@195.100.101.158:1521:cclab","scott","tiger");
PreparedStatement st=con.prepareStatement("insert into personal values(?,?,?,?,?,?)");
st.setString(1,user1);
st.setString(2,pwd1);
st.setString(3,"25");
st.setString(4,"hyd");
st.setString(5,email1);
st.setString(6,"21234");
st.executeUpdate();
con.close();
}
catch(SQLException s)
{ out.println("not found "+s);
}
catch(ClassNotFoundException c)
{
out.println("not found "+c);
}
} }
web.xml:
<web-app>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>init1</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>Ini</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>init1</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/regis</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
OUTPUT:
 |
| http://wikibrand.blogspot.in |
 |
| http://wikibrand.blogspot.in |
 |
| http://wikibrand.blogspot.in |
 |
| http://wikibrand.blogspot.in |
 |
| http://wikibrand.blogspot.in |
 |
| http://wikibrand.blogspot.in |
 |
| http://wikibrand.blogspot.in |
 |
| http://wikibrand.blogspot.in |
RESULT:
Thus a table is created and the details are entered into the table using jdbc from the registration form successfully.
Comments
Post a Comment